Meteorological Data Requirements |
|||
 Previous |
 Next |
|
|
File characteristics and projection
HYSPLIT requires that meteorological data fields be projected on a conformal map projection (Polar Stereographic, Lambert, or Mercator) or a regular latitude-longitude grid. The data must be organized with one record per variable per level and all records must have the same record length. Records are written in a forward time sequence. More details on the format and packing of the meteorological data can be found in the HYSPLIT User's Guide.The \exec directory contains several command line programs (chk_data, chk_rec) that can be used to analyze a HYSPLIT compatible meteorological data file. chk_file has been incorporated into a HYSPLIT GUI under the Meteorology / Display Data menu.
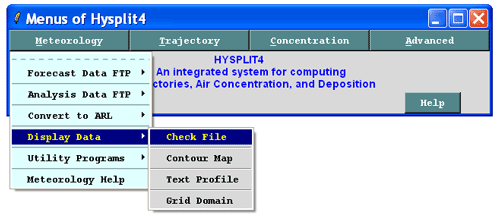
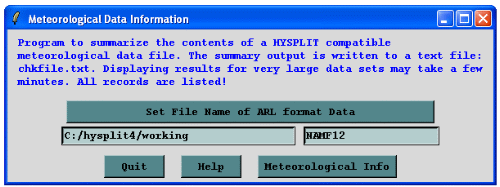
Running Check File prompts the user for the location of a HYSPLIT compatible dataset. (It is best to store all HYSPLIT compatible data sets in a directory whose name does not contain spaces as these can confuse the TCL scripts).
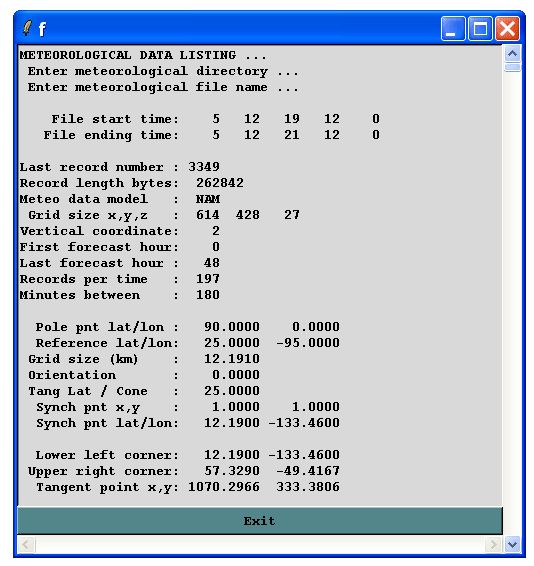
Meteorological Variables
A unique 4-character string identifies meteorological variables. The minimum requirements to run the model are the U and V wind components (UWND, VWND), ambient temperature (TEMP), height (HGTS) of the data level (if on pressure coordinates), and the surface pressure (PRSS). A sample extract of section 2 of the chk_file program is shown below for the NAM 12 km dataset for levels between the surface and 925 hPa.
Index Level # Variable listing and checksum values
.....
5 925.0000 7 UWND 108 VWND 236 HGTS 230 TEMP 123 WWND 82 RELH 20
TKEN 47
4 950.0000 7 UWND 147 VWND 129 HGTS 103 TEMP 89 WWND 155 RELH 121
TKEN 86
3 975.0000 7 UWND 47 VWND 209 HGTS 178 TEMP 193 WWND 125 RELH 252
TKEN 82
2 1000.0000 7 UWND 49 VWND 234 HGTS 138 TEMP 124 WWND 234 RELH 62
TKEN 198
1 0.0000 14 SHGT 101 MSLP 235 TPP3 184 CPP3 184 T02M 215 RH2M 41
U10M 119 V10M 212 PRSS 53 LHTF 120 SHTF 206 USTR 215
RGHS 177 DSWF 194
Data Records
Each data record is composed of a 50 byte ASCII header portion, describing the data packing, followed by the packed data of length (I*J bytes). A one-byte per element “difference packing” is used for all data fields. The first data record (INDX) of each time period contains information on the variables, levels, grid, and checksums. A sample extract of the final section from the chk_file program is shown below for the NAM 12 km data set.
# YYMMDDHHFHLLGG FLD EXP PRECISION VAR(1,1)
1 5121912 0 099INDX 0 0.0000000E+00 0.0000000E+00
2 5121912 0 099SHGT 11 0.8062992E+01 0.0000000E+00
3 5121912 0 099MSLP 4 0.6299213E-01 0.1016970E+04
4 5121912 0 099TPP3 1 0.7874016E-02 0.0000000E+00
5 5121912 0 099CPP3 1 0.7874016E-02 0.0000000E+00
6 5121912 0 099T02M 4 0.6299213E-01 0.2983304E+03
7 5121912 0 099RH2M 6 0.2519685E+00 0.8621770E+02
8 5121912 0 099U10M 4 0.6299213E-01-0.7976649E+01
9 5121912 0 099V10M 4 0.6299213E-01 0.1462120E+01
10 5121912 0 099PRSS 7 0.5039370E+00 0.1017162E+04
11 5121912 0 099LHTF 9 0.2015748E+01-0.1431365E+03
12 5121912 0 099SHTF 9 0.2015748E+01-0.1035156E+02
13 5121912 0 099USTR -25 0.1173320E-09 0.1000000E+00
14 5121912 0 099RGHS -2 0.9842520E-03 0.1590000E-04
15 5121912 0 099DSWF 7 0.5039370E+00 0.0000000E+00
16 5121912 0 199UWND 4 0.6299213E-01-0.9166061E+01
17 5121912 0 199VWND 4 0.6299213E-01 0.1795837E+01
18 5121912 0 199HGTS 5 0.1259843E+00 0.1470268E+03
19 5121912 0 199TEMP 4 0.6299213E-01 0.2967743E+03
20 5121912 0 199WWND -6 0.6151575E-04 0.8997059E-03
21 5121912 0 199RELH 6 0.2519685E+00 0.8856895E+02
22 5121912 0 199TKEN 4 0.6299213E-01 0.5000000E+00
23 5121912 0 299UWND 4 0.6299213E-01-0.9460953E+01
24 5121912 0 299VWND 4 0.6299213E-01 0.1790451E+01
25 5121912 0 299HGTS 5 0.1259843E+00 0.3694624E+03
26 5121912 0 299TEMP 4 0.6299213E-01 0.2946380E+03
27 5121912 0 299WWND -5 0.1230315E-03 0.1221895E-02
28 5121912 0 299RELH 6 0.2519685E+00 0.9656725E+02
29 5121912 0 299TKEN 5 0.1259843E+00 0.7500000E+00
........
Concatenating Meteorology Files
HYSPLIT compatible meteorology files can be concatenated by using the UNIX
cat or DOS type command.
For example, to concatenate file2 to the end of file1 in a DOS window type:
and for UNIX type:
 Previous |
 Next |