Computational Methods |
|||
 Previous |
 Next |
|
|
LAGRANGIAN APPROACH
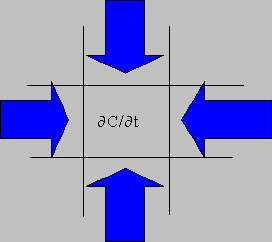
- Local derivative
- Solve over the entire domain
- Ideal for multiple sources
- Easily handles complex chemistry
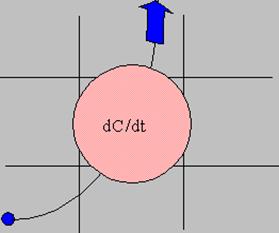
- Total derivative
- Solve only along the trajectory
- Ideal for single point sources
- Implicit linearity for chemistry
In the Eulerian modeling approach, air concentrations are computed for every grid cell by integrating the pollutant fluxes at each grid cell interface due to diffusion and advection. In the Lagrangian modeling approach, air concentrations are computed by summing the contribution of each pollutant puff that is advected through the grid cell as represented by its trajectory. In a Lagrangian model, modeling the growth of the pollutant puff’s 2nd moment or explicitly modeling the growth of a cluster of particles can simulate dispersion. Contrary to its acronym, HYSPLIT can simulate a pollutant distribution starting with a single particle or puff, or by following the dispersive motion of a large number of particles.
 Previous |
 Next |