Trajectory Example Calculation |
|||
 Previous |
 Next |
|
|
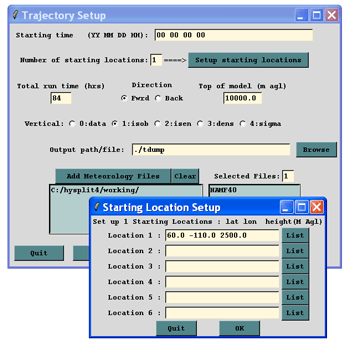
A pollutant particle’s transport can be illustrated by a trajectory calculation. For this example:
- Set the source location to 60N and 110W,
- set the starting height to 2500 m AGL, which is the approximate height of 700 hPa level (obtained by finding the estimated surface height from the meteorological profile program and subracting it from the height of the 700 hPa level),
- set the trajectory duration to 84 hours,
- set the vertical motion method to isobaric,
- and set the meteorological data to the NAMF40.
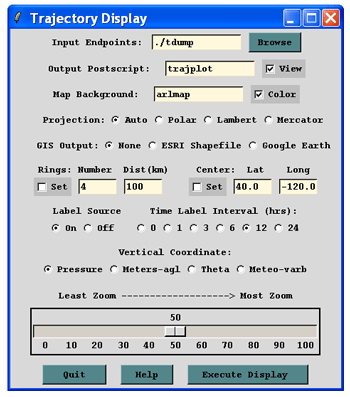
In this way we can compare the trajectory result to the 700 hPa height fields. When properly configured, the GUI menu should be similar to that shown below on the left. Then press Save to close the menu and then Run Standard Model. After the run has completed, press Trajectory Display, select any special options, and then Execute Display.
 |
 |
| CONTROL file |
The resulting graphic should look like the following:
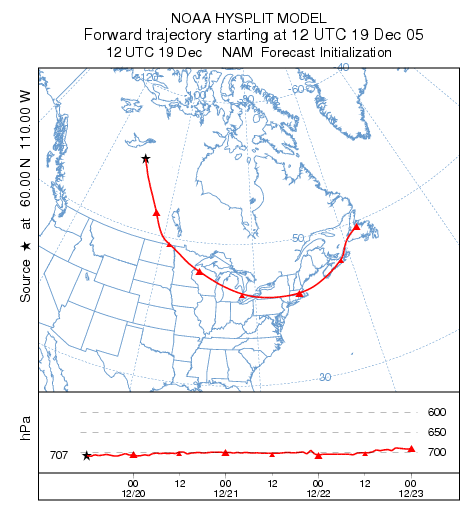
The relationship of the trajectory to the temporal and spatial variations of the 700 hPA height field is illustrated in the attached animation which was created using only the standard tools that come with HYSPLIT. These procedures will be discussed in more detail later. In addition, there are several optional tasks that can be completed to become more familiar with some of the trajectory display program options:
- Run this case from the command line,
- draw concentric distance circles on the map,
- and force the map center to a different location.